Using Smart Meters and intelligent recloser to improve Power Quality in distribution networks
Problem Statement & Gaps in Understanding:
Individual Thesis Topic Aim and Objectives:
Literature Review and Preparatory Theory and Definitions
Smart Meter Function & Data Usage
Smart Meter Communication | Common Section used between Group Members
Section Three: Intelligent Recloser
Comparison between the Intelligent Recloser and Traditional Circuit Breaker
Examples of Intelligent Reclosers and their Communication Capabilities
Overview of Relevant Local and International Power Quality Standards
FLISR/FDIR (Fault Location Isolation Supply Restoration)/(Fault Detection Isolation Restoration)
Definition of the Self-healing Process/FLISR Operation
Illustration and Breakdown of the FLISR Process
Existing Set-ups and Implementations
Active Volt-VAR Control and Power Factor Control
Integration of Renewable/Distributed Sources and Storage
Barriers and Challenges to Implementation
In response to rising pressure from global issues such as climate change and the technological and social attitude shifts towards clean energy and away from fossil fuels, the traditional power grid is quickly becoming obsolete.
With emerging technology and improved efficiencies in renewable power and governmental shifts towards a higher adoption of renewable and distributed sources, a more modern power distribution network which incorporates advances in microelectronics and software is needed.
On-top of this the increasing penetration of Renewable and Distributed sources such as solar, wind, hydro and consumer side products (“Tesla Powerwall” and roof-top solar) into existing power grids have a disruptive effect on measures of power quality such as mains frequency and voltage and must be accounted for.
Alongside this, growing fields of complementary research into micro-grids, renewable technology, and energy storage have spurred the shift towards smarter power distribution networks. Therefore further research into the “smart grid” and in turn the key electronic devices such as the Intelligent Recloser that comprise the smart grid is needed.
Currently the technological capabilities of IEDs (Intelligent Electronic Devices) as well as advancements in microprocessor technology and microsystems related to monitoring, sensing and software have all advanced to a point where a smart grid is not only technologically feasible but the next logical step.
However the adoption and implementation of a smart grid is hampered by gaps in the understanding of certain key elements that constitute a “smart grid” such as the Smart Meter and Intelligent Recloser.
Some of the gaps that will be covered in this thesis report are listed below:
To build an in-depth understanding of how IEDs (Intelligent Electronic Devices) such as the Smart Meter and Intelligent Recloser can be utilised to improve power quality in the emerging “Smart Grid” power distribution network.
Focus in-depth on how the Intelligent Recloser functions and how it can be used to improve power quality in a “Smart Grid”.
An electrical grid is made up of 3 components and these are listed below as:
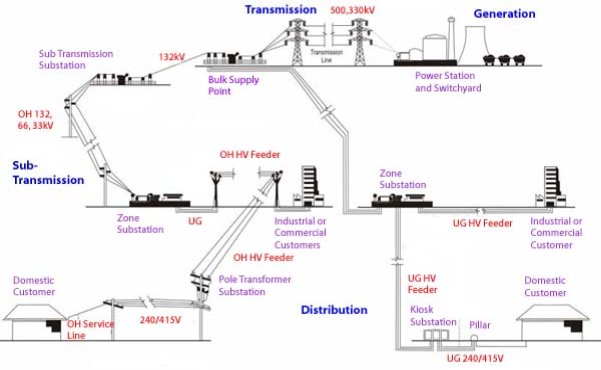
Figure 1. Basic Structure of Electric System[8]
Figure 1 shows the basic structure of an electric grid and where each of the three components are in the system. Power distribution and transmission make up most of the electric grid. These are possible using substations which act as nodes for different voltage levels. These nodes are connected to transmission lines and form the whole electric network.
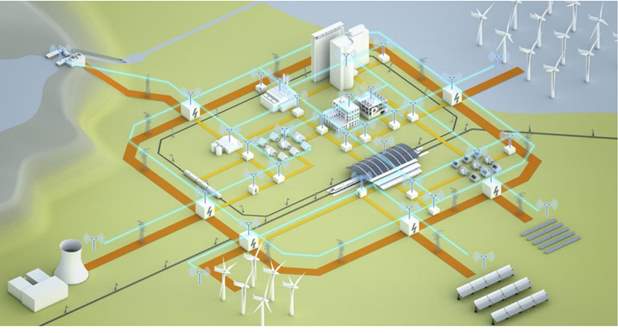
Figure 2. A Smart Grid (Siemens Energy Sector, 2014, p. 6)
A Smart grid is the next logical step-up from the traditional power grid; enabled by advances in technology and composed of ‘smart’ components such as smart meters and intelligent reclosers; the Smart grid promises improvements in efficiency, power quality as well as the integration of upcoming renewable power generation and storage elements as seen in Figure 2. Smart grids as opposed to traditional power grids are bidirectional in terms of the incorporation of data alongside power in the lines, thus opening the possibility of two-way communication between control systems at power stations/substations and street/local level smart components such as intelligent reclosers and smart meters. In a smart grid, power transmission and distribution is made automatic.
Intelligent power transmission is primarily implemented at substations. Various primary and secondary equipment is required, as well as a monitoring system in order to implement intelligent power transmission.
The ‘intelligence’ of intelligent power transmission is mainly reflected in the real-time status checking of equipment, panoramic monitoring, diagnostic evaluation, one-button sequence operation, automatic fault handling, intelligent inspection, auxiliary decision making etc. If all substations in a regional grid have implemented this system, the grid is likely to emerge as a major global innovation.
Intelligent distribution is for serving both the grid practitioners and the end users. It is mainly implemented through some mechanism to make power generation and distribution more automatic. Through this mechanism end users would be able to participate in the coordination and optimisation of distributed network resources.
| Compare | Traditional Grid | Smart Grid |
| User participate | Almost none. Only expected to pay the bill. | The user will be an integral part of the power system. Encourages and promote s the user to participate in their own operation and management. |
| Smart device | None | Two-way communication. Smart device will bring their own WIFI. The user’s electricity information will be sent to the power supply company network data terminal. Power supply companies will classify this data, do comparative analysis, and then according to the actual situation of the user, an electricity program will be tailored to them. Users can see the actual percentage energy usage of all devices in their home |
| Improve measure efficiency |
You have to be 100% sure of the quality of your product to give a money-back guarantee. This describes us perfectly. Make sure that this guarantee is totally transparent.
Read moreEach paper is composed from scratch, according to your instructions. It is then checked by our plagiarism-detection software. There is no gap where plagiarism could squeeze in.
Read moreThanks to our free revisions, there is no way for you to be unsatisfied. We will work on your paper until you are completely happy with the result.
Read moreYour email is safe, as we store it according to international data protection rules. Your bank details are secure, as we use only reliable payment systems.
Read moreBy sending us your money, you buy the service we provide. Check out our terms and conditions if you prefer business talks to be laid out in official language.
Read more