CLEAN TECHNOLOGY AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT 2019-20
Resource-product-waste Cycle for Papers
In, the Aims and the objectives of this Essay is based on main points about the resource of the papers, paper product and papers waste cycle, the impacts on the environment and what the options to avoid this impacts. generally, according to the researchers, the papers products is an easy material to recycle, recover and reuse, in addition, less industry pollute and effect on our environment if we compared with other materials like plastic and metal products, but the main impact from this industry on forests(the woods), because it is the raw material and this can cause problems on our natural resources and change on the climate.
Table of Contents
The Resources and Raw materials
Paper products and manufacture
Conclusions and Recommendation
The paper industry is one of the largest in the world, with global paper production in 2013 Approximately about 403 million tons. (Pratima Bajpai, 2016). It is command and control mainly by the United States, Canada, Finland, Sweden, Japan and some country like India and China are expected to be key in this industry’s growth over the near future. (Pratima Bajpai, 2012).
The process of making paper became highly cost-sensitive, and the result of this increased productivity and quality of the paper, connected with environmental regulatory pressures, Most of the manufacturing facilities in the paper industry are accommodate and link with another industry. Paper industry begins with wood chipping at the front end, followed by pulping, bleaching, papermaking, and recycling of post-consumer products. (Pratima Bajpai, 2016).
According to Pratima Bajpai, the chemicals and technologies that used in the manufacturing papers expected to open new opportunities for the growth of the market. in addition, technological innovation, focusing on sustainable processes to minimise environmental impact is expected to be the most important factor for market development. (Pratima Bajpai, 2016).
In this Essay, I will descript the most stages and life cycle of the paper, start by the main resources and raw material of the papermaking and I will focus on the most important resources(the wood fibre). Then descript the main manufacture processes, finally, the disposal of papers and will consider the environmental impacts at each stage and the options for reducing waste and pollution, and the opportunities can be used to converting wastes to resources.
The paper basically is made from pulp, this pulp can be made from wood,cotton, waste and other materials but the wood is main original raw material, this main raw material produces the resources of paper called cellulose comes from the fibre of the wood. The Cellulose fibre normally can find in many vegetable tissues extracted by mechanical or chemicals. (2)
There is numbers of species yielding fibre can be used for paper but in practice fibre suitable for paper can be extracted from only a few trees species, they are softwoods, hardwoods, straw, esparto grass, bagasse and bamboo. In addition, papermaking fibre is derived from cotton, linen, abaca and sisal (1).
Around 90% of the wood used by the European paper industry comes from European forests, because of that the European paper industry is strongly committed to sustainable forest management system and uses wood certified to PEFC and FSC standards, this a certification system help the sustainable management of the forest and control the industry that uses the forest as a main raw material.(2)
There are environmental impact in paper industry because the main resource of this industry come from nature(forest fibres) and because of that the European paper industry consider the bio-based economy it takes all the components in wood and transforms them into value-added bio based products not only looking for pulp and paper but also consider the biorefinery concept, such as , while wood fibre is used to make pulp, resins can be turned into chemicals and bark into renewable energy and resources, and can be process steam use to heat homes, and this the good idea and options to reducing waste and pollution coming from this industry, Europe’s paper industry provides the ideal path from a fossil-based to a bio-economy.(2)
There are a lot off paper products, generally, are categorized into five main categories, newsprint and magazine papers, printing and writing papers, sanitary and household, paper packaging materials and products and other specialised paper.
The paper industry is one of the biggest and important industries in the world, around 400 million tons produced annually. (9) The Paper Manufacturing is a huge process that can be divided into two groups, the first for the manufacturing of pulp and paper and the second for the manufacturing of converted paper products.
According to Pratima Bajpai, the paper is made in different stages(table 1)
|
Operation |
Processes |
|
Raw material preparation |
|
|
Pulping |
|
|
Chemical recovery |
|
|
Bleaching |
Mechanical or chemical pulp bleaching |
|
Stock preparation and papermaking |
|
Table 1 Steps involved in the manufacturing of paper, Pratima Bajpai (2015).
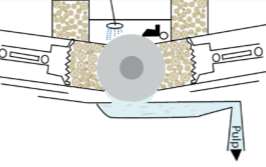 the wood is first processed so that the fibres are separated from the unusable fraction of the wood, the pulp making can be done mechanically through mechanical pulp((figure1 ) groundwood pulp, refining pulp, use a rotary millstone, to make the process easy they use the addition of water. and to cool down the millstone. The pulp is then filtered to ensure that the final pulp contains only cellulose fibre. in the end, the pulp is cleaned to remove sand or dust. (13)
the wood is first processed so that the fibres are separated from the unusable fraction of the wood, the pulp making can be done mechanically through mechanical pulp((figure1 ) groundwood pulp, refining pulp, use a rotary millstone, to make the process easy they use the addition of water. and to cool down the millstone. The pulp is then filtered to ensure that the final pulp contains only cellulose fibre. in the end, the pulp is cleaned to remove sand or dust. (13)
Figure 1 Mechanical pulp, (SCA, 2010)
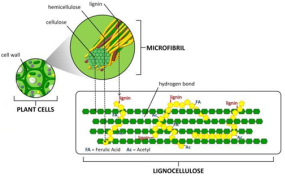
Also there chemo-mechanical pulp (figure 2), the chemical used to break down the lignin, that lignin bind celluloses fibres together, this process made under temperature 150°C – 200°C. in the end, the pulp is filtered and cleaned. (13) SCA, 2010)
Figure 2 Chemi-mechanical pulp, (SCA, 2010)
In all methods, the temperature is increased to soften the lignin or can be done chemically( kraft, soda, and sulphite) under elevated temperature and pressure to extract pulp fibres, then bleached and further processed, depending on paper required. (9) In the paper factory, the next step is dried and pressed to produce paper sheets. (figure 3)
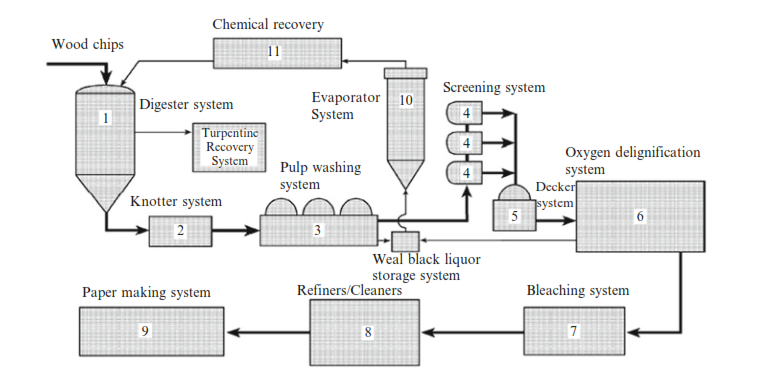
Figure 3 Overview of the kraft pulping mill with papermaking system, USEPA ( 1998 )
Some integrated pulp and paper mills manage multiple operations such as the chemical pulping, bleaching, and papermaking. The pulp needs washing to get pulp free of unwanted chemical solubles. (9) This one of environmental impacts for this industry, how and where to discharge the chemicals after use(pollutant discharges and emissions).
the most basic method is the replacement of the contaminated liquor accompanying the pulp fibres by using clean water, the most common washing technology is rotary vacuum washing, carried out in two, three, or four washing units. (9). (figure 3, 4)
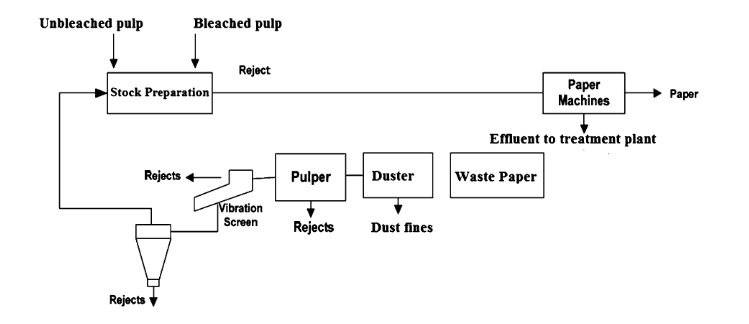
Figure 4 Diagram for a typical papermaking process, Pratima Bajpai (2015).
According to CEPI, 56% of the pulp and paper mill energy consumption is bioenergy and this equating to 20% of European bioenergy consumption, 1m³ of wood, the industry creates 2.38 times more products and energy as compared to using that cubic meter in a single use. (2)
Pulp and paper mills manufacture are ideal sites for biorefineries. Because paper and forest products companies are efficient growers, harvesters, transporters, and processors of biomass; pulp and paper mills are located near different sources of biomass, such as forest and agricultural residuals, and energy crops. (Connor, 2007)
The paper industry can cause pollution and environmental impacts through dust, fumes and gases, water pollution from contaminated and chemical solvents, result from the pulping and bleaching processes (the chemical pulp manufacturing), noise pollution from materials handling and deliveries(7, 9).
The EU and UK made regulations to control this pollution, the EU, through European environment agency made integrated pollution prevention and control regulation(Directive, 96/61/EC). (10). In the UK The Pollution Prevention and Control 2011 in England and Wales, in Scotland Regulations 2012 (PPC 2012) to implement the requirements of the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), aim to remove ambiguities and inconsistencies, ensure clearer environmental benefits, promote cost-effectiveness and encourage technological innovation. (8)
The recycling and recovery of paper continue to grow in the world, especially North America, that helps to reduce the high environmental impacts and costs of disposing of paper in landfills. In U.S. paper recovery rate increased from 46% in 2000 to 63.4% in 2009. In Canada, the reported paper recovery rate in 2009 was 66%.8.(11).
In In European paper recycling rate increased from 71.5% in 2015 to 72% in 2016 and increased to 72.3% in 2017 is a significant step forward for paper recycling in Europe, European Declarations on Paper Recovery and Paper Recycling have the plan to reach the new target of a 74% recycling rate by 2020.(12)
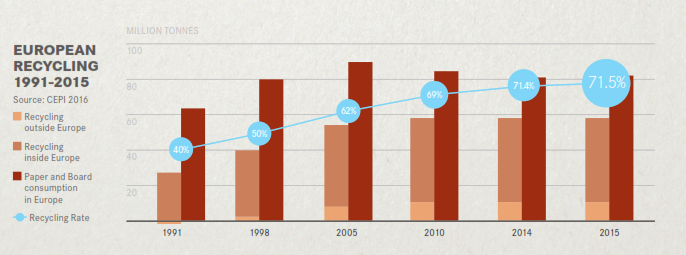
Figure 5 European paper recycling rate 1991-2015, (EPI 2016)
Most of papers products are recyclable, such as cardboard, newsprint, and office papers. but also there is non-recyclable Paper like craft envelopes, carbon paper, paper towels and tissues.
According to, Rick Leblanc. (2018), The paper recycling process has a number of steps:
There are some solutions to avoid the impact of this industry, According to Chambost .V , Paper and Pulp companies need to considered one of the general the biorefinery concept, Firstly , biorefinery configurations that try to transform biomass into biofuels, and potentially benefit from an improved carbon footprint and carbon credits and its impacts on climate change, Secondly, Biorefineries that try to capitalise on the emerging huge biofuels market by produce ethanol or diesel production (Chambost et al., 2008).
The policy regulations, such as, integrated pollution prevention and control regulation(EU, UK) to control this pollution, uses wood certified(PEFC, FSC) standards to manage the forest and control the paper industry that uses the forest as a main raw material.
In addition, reuse or use alternative material that has less effect on our environment.
In this report, I have identified the resources, manufacture and disposal of the paper industry and the environmental impact of resources and processes, the chemical and wastewater is the major source of polluting materials from the pulping and bleaching processes in this industry.
One of the easy solutions by recycled cellulose fibres to reduce the quantity of water because the paper papermaking processes use a lot of energy and water, we need a real implementation of the regulations and environmental policy is important to reduce the impact from this industry on the environment.
We need more research on using clean technology and about environmental impact and savier and easiest solutions for this pollutant impacts.
You have to be 100% sure of the quality of your product to give a money-back guarantee. This describes us perfectly. Make sure that this guarantee is totally transparent.
Read moreEach paper is composed from scratch, according to your instructions. It is then checked by our plagiarism-detection software. There is no gap where plagiarism could squeeze in.
Read moreThanks to our free revisions, there is no way for you to be unsatisfied. We will work on your paper until you are completely happy with the result.
Read moreYour email is safe, as we store it according to international data protection rules. Your bank details are secure, as we use only reliable payment systems.
Read moreBy sending us your money, you buy the service we provide. Check out our terms and conditions if you prefer business talks to be laid out in official language.
Read more