LASA 2: Organization Website Review
Summary
This report will discuss the background history of an international organization named IKEA. This report will obtain impressions of the organization corporate website, as well as give analysis of the organization’s vision, mission, and goals. The report will also analyze the organization’s strategic approach to globalization and their approach to competition, sustainability, CSR, marketing, analysis (external, internal, and industry), and cross border issues. Within the report the organization’s financials will be examined, including their most recent annual report and a review of the profit margin statement from the CEO. The organization’s Corporate Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility Policy will be evaluated as well. There will be an organizational assessment discussed using the SWOT analysis to show the organization’s strengths, weakness, opportunities, and threats. Also, an explanation will be given of the organization’s capacity to be able to fulfill strategic missions while increasing profit margin.
Introduction
IKEA was established in 1943 in Sweden though Ingvar Kamprad. Kamprad was conceived in 1926 as child of an agriculturist in Smaland, a place in southern Sweden. At 17 years old, Kamprad chose to become a business visionary and created an industrial organization called “IKEA”. The word IKEA was an abbreviation of his name and address: Ingvar Kamprad and Elmtaryd, Agunnaryd, which was at one time the distinguish of his homestead and the identity of the town it was located within. Based in Denmark, IKEA International is one of the world’s pinnacle outlets of furniture, home goods, and housewares. The organization structures its very own products and sells them in more than 330 IKEA stores that spreads throughout approximately 40 different countries worldwide, with approximately 154,000 employees. The organization also promotes its stock through mail-order, distributing its thick catalogs once every 12 months in the areas surrounding its store locations. IKEA is described by its endeavors to offer high-quality products at very low prices. To save money for the organization and its customers, the organization purchase products in bulk, ships, and stores products unassembled utilizing flat bundling, and has customers assemble many products in the privacy of their own home (Strandvej, 2018).
Corporate Website
Upon visiting the organization’s website, I was a bit surprised that the website didn’t stand out with vibrant colors and large pictures of products it offers. The website is plain, yet informational. The corporate website offers information about the inside of the organization, current year financial summary, vision and business ideas of the organization, sustainable growth, key figures, and ownership and structure. The website also offers useful links that direct viewers to store information, such as opening hours, contact, and restaurant information. There are also links to direct viewers to all the furniture the organization offers, catalogues, services, planning tools, jobs, FAQ’s, and contact information. The website also has links to the organization social media platforms, such as; Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest, YouTube, and the organization’s newsroom. The website offers a link to view the IKEA Foundation, as well as the organization’s responsible disclosure. The website is very informative and offers all details around the organization. The website is a secure website with the ability to view the Modern Slavery Statement, Privacy Policy, Cookie Policy, Terms of use, Terms and Conditions, Accessibilities, and the option to change the country so that viewers can view the corporate website within their current region.
Vision, Mission and Goals
In 2013, IKEA’s mission scored 2 out of 4.5, which implies that the organization did an unfortunate job creating its mission statement. The statement lacked 5 components: markets, innovation, concern for survival, public image and employees. It didn’t make reference to any qualities that were used in its assessment and didn’t address any stakeholders with the exception of its customers. IKEA’s mission is customer-oriented, which implies that the organization focuses on the fulfillment of customers and tackling their issues. The most serious issue with organization’s mission is that it’s likewise used as a vision, which is a different statement articulating its own purpose. Currently, the statement ineffectively conveys IKEA’s core purpose to its stakeholders (Jurevicius, 2013). As of today, both the vision and the mission statement connect to the overall corporate goals. The vision encourages customers and stakeholders, while motivating employees to accomplish goals. The mission statement interconnects the goals of the organization to customers, all stakeholders, and employees. IKEA’s goal is to deliver quality home goods at reasonable prices. The reasoning behind all the advancement of IKEA’s products is that low prices make very much structured home goods accessible to everyone. IKEA’s goals are to continually do everything “a little better, a little simpler, more efficiently and always cost-effectively” (“Vision – Vision, Values and Mission in Driving Strategy – IKEA”, 2018).
Globalization
In 1998, IKEA began its retail tasks in China. To meet local laws, it shaped a joint project. The project filled in as a decent stage to test the market, comprehend local needs, and adjust its procedures in like manner. It saw right off the bat that Chinese apartments were small in size, and customers required useful, secluded solutions. The organization made slight changes to its furnishing to address local needs. IKEA confronted comparable issues beforehand when it entered the United States. The organization first attempted to reproduce its current plan of action and products in the US., yet it needed to modify its products based on local needs. American customers, for example, requested larger furnishings and larger storage rooms. IKEA had to make various changes to its showcasing technique in the US. The difficulties it came upon in China, however, were far greater than the ones in the US. IKEA recognized the vital difficulties and made endeavors to beat them. One of the fundamental issues for IKEA was that its costs, measured low in Europe and North America, were higher than normal in China. IKEA manufactured various processing plants in China and increased local tracking of materials. While globally 30% of IKEA’s range originated from China, about 65% of the volume revenue in the nation originated from local sourcing. The local manufacturing plants settled the issue of high import taxes in China (Chu, Girdhar & Sood, 2013).
IKEA additionally needed to change its advertising methodology. In many markets, the organization utilizes its item list as a noteworthy promoting apparatus. In China, notwithstanding, the index gave chances to competitors to mirror the organization’s items. Undoubtedly, nearby competitors replicated IKEA’s structures and afterward offered comparable items at lower costs. IKEA chose not to respond, as it understood Chinese laws were not sufficiently able to discourage such exercises. Rather, the organization is utilizing Chinese social media and micro-blogging website Weibo to focus on the urban youth. IKEA also balanced its store area system. In Europe and the US, where most customers utilize personal vehicles, IKEA stores are normally located in suburbia. In China, however, most customers utilize public transportation, therefore, the organization set up its outlets on the edges of urban areas which are associated by rail and metro systems (Chu, Girdhar & Sood, 2013).
IKEA has built up a manageability methodology that incorporates individuals and planet. The procedure comprises of various long-haul key objectives to improve IKEA’s effect on networks and nature by 2020. For example, IKEA needs to deliver as much sustainable power source as it devours by 2020. To guarantee that it is on track, IKEA has created achievement objectives that it can use to gauge its progress in shorter eras. All through this procedure, IKEA needs to be straightforward with its stakeholders, giving regular divulgences about its progress.
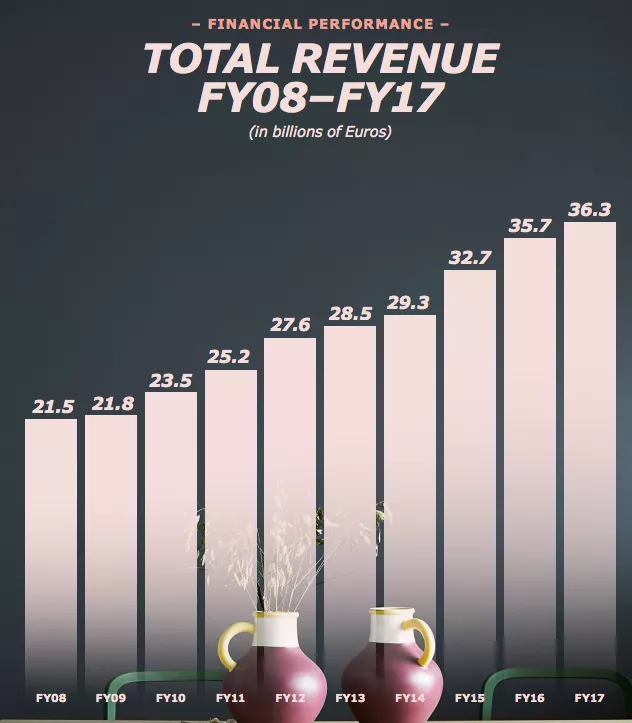 Financials
Financials
Since 2000, IKEA has cut its costs by over 60%. The organization intends to decrease costs further, helped by large scale manufacturing and trimming production network costs. As can be seen in the picture above, IKEA has continued to gain revenue each year in its overall total revenue. For the financial year of 2017, the IKEA Group reports a total retail sale of $40.2 billion (EUR 34.1 billion). After reviewing the organization’s recent financial report and the profit margin statement presented from the CEO, I draw a conclusion that the organization has a great marketing plan to conquer success for years to come. The organization understands that there will be failures along the way, however it continues to strategize plans and techniques to overcome all obstacles as they occur. The organization also continues to invest in stakeholders while making needed expansions so that the organization, stakeholders, employees, and customers will all gain in the end.
Corporate Ethics and Social Responsibility Policy
IKEA’s ethics program has training for employees as well as codes and policies to guide ethical conduct. Perhaps its most essential code of conduct, however, is its code of conduct for suppliers. A portion of IKEA’s most ethical troublesome risks are with their suppliers. Since such a large amount of IKEA’s business includes acquiring products, materials, and services, IKEA has embraced a strong code of ethics it calls the IKEA Way, or IWAY. IWAY outlines the organization expectations of suppliers. Those observed to be infringing upon of IWAY could be dropped as a supplier. The primary necessity that potential suppliers will see before they do business with IKEA is that the supplier cannot utilize constrained or child labor. Also, IWAY requires that the suppliers themselves relegate at least one person whose duty will be to guarantee that the supplier is adhering with IWAY expectations. Any sub-contractors the supplier utilizes must sign a document to witness that their organization will also adhere with these norms. The supplier must likewise consent to an internal compliance assessment every 12 months.
IKEA wants to comprehend its employees and their perspectives toward the workplace environment. The organization utilizes an autonomous third organization to direct VOICE, a colleague survey to interpret employee perspectives and their fulfillment with the organization’s business activities. Helping employees to comprehend their sustainability goals is essential to IKEA, which has driven them to create sustainability training materials for employees. IKEA has built a corruption policy called Rules of Prevention of Corruption and an investigation policy giving rules employees can use for acceptable behavior in the wake of noticing questionable activities. IKEA has also created a trust line that permits employees to report any issues or concerns to the organization.
SWOT Analysis
Dudovskiy’s (2017) article states the following regarding IKEA’s SWOT Analysis:
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
Profit Margin
IKEA has the capacity to fulfill its strategic missions while increasing profit margin by continuous expansion domestically and internationally in the field of retail.
Conclusion
IKEA has a strong reputation for selling quality products at low prices. a solid notoriety for moving quality items at low costs. The organization’s capacity to concoct imaginative structure ideas and keep costs low furnish it with a noteworthy upper hand. The organization is exceptionally well known in Europe and the United States. It has likewise shown a solid inclination toward altruism, development, and maintainability. IKEA has strong ethical qualities that it uses to control organization choices. These qualities seem to reverberate with employees and consumers alike as many are extremely faithful to IKEA. IKEA must keep a solid quality-based culture while additionally cautiously observing its activities in various nations.
References
You have to be 100% sure of the quality of your product to give a money-back guarantee. This describes us perfectly. Make sure that this guarantee is totally transparent.
Read moreEach paper is composed from scratch, according to your instructions. It is then checked by our plagiarism-detection software. There is no gap where plagiarism could squeeze in.
Read moreThanks to our free revisions, there is no way for you to be unsatisfied. We will work on your paper until you are completely happy with the result.
Read moreYour email is safe, as we store it according to international data protection rules. Your bank details are secure, as we use only reliable payment systems.
Read moreBy sending us your money, you buy the service we provide. Check out our terms and conditions if you prefer business talks to be laid out in official language.
Read more