This assignment will look at the vital role that managers and leaders play in the operation of an organisation and how this componence work together to utilise various resources through strategic and models to see that the organisation benefit in achieving their objectives and goals that have set. This assignment will hopefully evaluate the different types of management and leadership skills that are in practice within an organisation and the individual strengths and weaknesses that arise with each method. There will also be a look at the managerial and operational needs that vary from organisation to organisation, all depending on the circumstances of the organisation and the variety of the management and leadership skills.
LO1 & LO2 Differentiate between the role of a leader and the function of a manager
Apply the role of a leader and the function ofmanagers in given contexts
P1. Define and compare the different roles and characteristics of a leader and a manager.
Manager: Managers are the people who drive the goals and objectives of the company by the pre-determined plans that have been assigned to them. To accomplish these task, managers have to develop and establish approaches to the organisation’s strategies and to ensure that the planning of the workforce performs in a way that meets the objectives of the organisation. The positive aspect of managers is that they can be distributed at various levels within the business which allows them to be able to manage the tasks across different departments. Managers will also have the responsibility of dealing with the appraisal of their team, the process of assessments will be based on the performances of an individual and how they perform their duty.
Leaders: Leaders are those who get the work completed from those employed by the business. Just as managers, leaders are an essential factor in the role of motivating the workforce through the use of their communication and leadership skills. They are skilled in making their team achieve their objectives and goals, the most favourable outcome of a leader is that they can influence and motivate an employee for them to perform at their level.
The various functions of management and leadership are shown below:
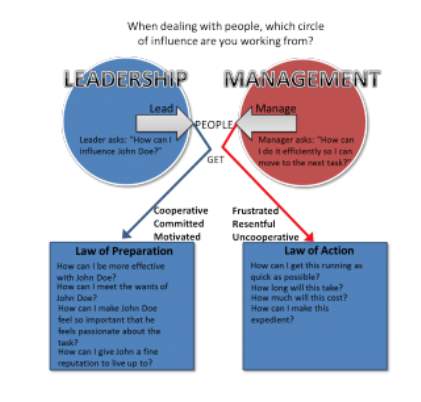
The above image shows the difference in the mindset of how a leader and manager operates.
Image 1: http://www.varsityfs.com/leader-or-manager-what-are-you/
Management: can be described as the area where managing all aspect of a department/team is needed in the best possible manner, this is a skill that is lacking to be able to get the work completed. One of the differences between management and leadership is that:
Leadership: A characteristic of inspiring people, who will be able to meet their objectives. Leadership is not precisely the same as management because direction is one of many elements of control.
Differences between managers and leaders
Often the roles of managers and leaders can be seen as an interchangeable factor, but there is a clear difference between these functions. Managers accomplish their task by setting out the objectives of the organisation while leaders are tasked with communicating the vision of the organisation which will inspire the workforce. The below table gives an example of the difference between the skills set of managers and leaders:
| Managers | Leaders |
| The task of setting the objectives of the organisation. | Bring around the objectives/goals being developed by the manager. |
| Policies have to be communicated to the leaders. | Communicating and influencing employees to work as per the given policies. |
| Direct their department. | Direct their team. |
| Creating a progression plan that will be used by the organisation. | Are given the task of implementing the goals set out by the organisation. |
| Primary focus on the goals and objectives of the organisation. | To focus on the workforce. |
| Able to contribute more to the planning of the organisation. | To inspiring the work environment. |
| In charge of directing the work to the team. | To motivating the employees to work. |
From the table above, it can be seen that there is an absolute difference between leaders and managers, even with this difference these individuals play an essential part in the success of the organisation. A fully informed leader and manager can see to it and provide the support that the business needs to ensure for the long run of their business and ensure that they stay ahead of their competitors.
The role of a leader can be seen as a decisive role as they ensure to look into the hidden talent of their team so that they can provide guidance to ensure that their goal is achieved not only for the business but the individual. As for managers, they can come across negatively as they can criticise their team, to a certain level, to be the best in the field but this action can sometimes be seen as demoralising the individual.
P2: Examine examples of how the role of a leader and function of a manager apply in different situational contexts.
P3. Apply different theories and models of approach, including situational leadership, systems leadership and contingency.
Situational Leadership: In the late 1970’s, Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard developed the situational leadership model, the development of this model came from the idea of managers and organisation being able to adapt to different styles of leadership according to different situations that would arise within a business. For any global company, conditions will occur within the organisation that would differ from time to time and are mostly out of the control of management. It’s seen as an essential factor that the style of leadership can adapt to these situations, so that is it able to provide the required solution for the organisation.
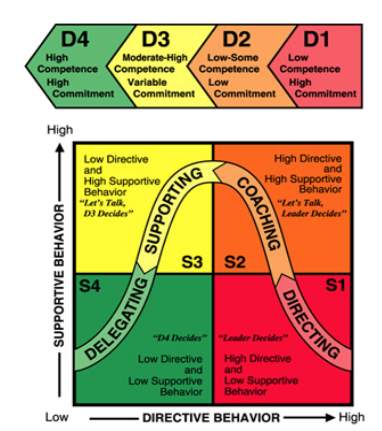 There are two factors which mainly drive the situational leadership model, the directive and supportive behaviour of leadership. The benefit of this model is to ensure that the organisation can adapt to various situations within the business and to provide that the decisions making of managers and leaders will assist in the growth of the company.
There are two factors which mainly drive the situational leadership model, the directive and supportive behaviour of leadership. The benefit of this model is to ensure that the organisation can adapt to various situations within the business and to provide that the decisions making of managers and leaders will assist in the growth of the company.
The Hersey and Blanchard model show the direct effect of the use of the situational leadership at different stages within an organisation.
Image 2: https://hubpages.com/business/What-is-the-Situational-Leadership-Theory
The sense of the above model is to be able to develop the communication skills that are required at all levels of management so that it guarantees the growth of the industry. This model provides leaders with the skills to navigate through the increase in the diverse work environment and the evolving market globally. When adapting to the circumstance that arises within the organisation, this model will ensure that leaders will be able to address the pressing trials that persistent in the organisation.
Systems leadership: The systems leadership outlines the guidance across the organisation and the geopolitical boundaries. The idea for this style is to ensure that leaders across the board not only look at their perspective or the company but to look at the boarder geopolitical development that would change to system and structured process of the business.
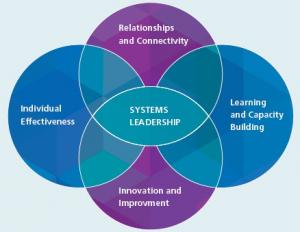
The above model shows cases the four drives towards system leadership.
Image 3: http://www.leadershipeastmidlands.nhs.uk/our-programmes-0
When applying this model, the organisation should seek towards appointing a leader who sees the long-term vision of the organisation because all leaders aim to ensure that their strategies and procedures can gain new heights and growth for the organisation.
Contingency Approach: Fiedler’s contingency leadership was created in the mid-1960s by a scientist who was studying the characteristics and personality of leaders. The theory is based on the factor that there isn’t just one kind of leadership model that is suitable for any organisation. It is a driven idea that the best possible course of action will all depend on the internal and external factors that affect the business and how a leader will appoint their decisions within this situation.
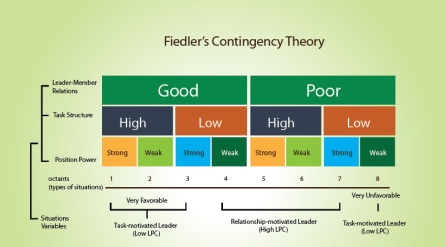
The above models show how the Fiedler’s contingency is used to decide the style of leadership that will influence the behaviour of a manager.
Image 4: https://www.tools4management.com/article/a-detailed-study-of-fiedlers-contingency-theory/
Before applying this model, the business has to examine the challenges which have arisen within the company so that they can ensure that the most suitable leadership style is picked so that it is useful in this situation. The outcome of this overall solution will be that the business will be able to benefit from the increase in employees productivity, the development of their work culture and a sense of motivation for their employees.
Chaos Theory: The chaos theory comes into action at particular points of time within the market, this model is mainly connected to the market when it is undergoing development, i.e. a slowdown in the global economy or a change in the demand from customers. It is managements point of view, to ensure that the organisation is capable of adapting to these changes so that they can avoid a loss to the business.
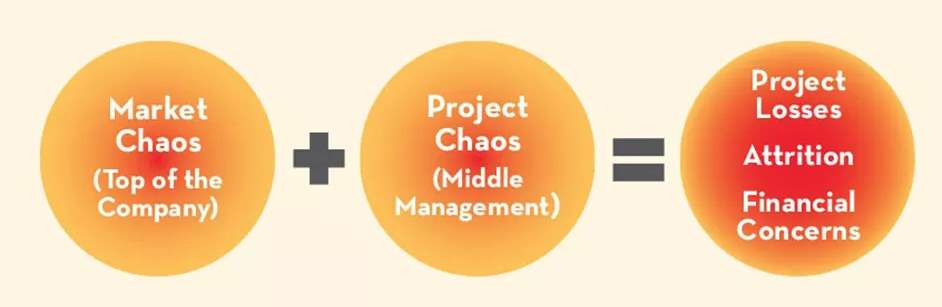
The chaos model showcases how the different marketing environment results in the chaos theory.
The two advantages that an organisation can benefit from when applying this theory is that management will see a more efficient and effective development of the adaptability skills of their employees. The outcome of this path is that there will be convenient ease in the way that employees react to the specific condition
Management by objectives: Management by objective is the model which aims to develop the performance and productivity of the business by defining what the goals are for the organisation, to ensure that these objectives are agreed upon and that these objectives are achievable by both parties.
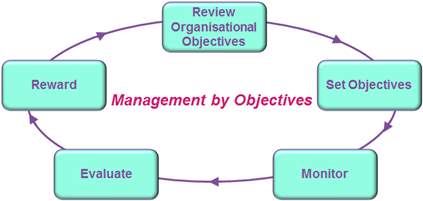
The Five stages that bring the management of goals into action for a business.
Image 6: https://www.pocketbook.co.uk/blog/2011/08/02/management-by-objectives/
By applying this model, management will be able to ensure that the tasks and objectives that are set will have a more methodical process to them. Employees will be fully assured of their roles and responsibilities while accomplishing this objective. This path could be seen as a positive approach to undertake for any organisation, as this will benefit the employee in being able to stay focus throughout the process which will guarantee growth for the organisation.
M1. Analyse and differentiate between the role of a leader and function of a manager by effectively applying a range of theories and concepts.
The various theories of leadership and management are discussed below:
Leadership theories:
1. The transformational leadership theory is described as the principle which guides the skills of leaders to causes specific changes to individuals, the work environment and even the local community which the business operates. Leaders will look at this factor to create a valuable and positive change in the workforce, the ultimate objective of the company is to be able to develop their employees into leaders. The transformational theory procedure for leaders is best suited for an organisation who aim to succeed at each point of their planning decisions to ensure that there is no shortage of leadership qualities and abilities in the organisation in the future.
2. Contingency theory of leadership is based on the approach to a particular situation at a specific time within the organisation. The method that is applied will be according to the condition that the business is experiencing at any given specific time. The contingency for leaders can be used at various times to circumstances such as to increase productivity from the workforce, to improve employees co-ordination when working in different groups, to ensure that employees take more responsibility for their work approach and to facilitate employee retention in the organisation.
3. The trait theory is based on the characteristics and qualities of a leader who leads efficiently, but this theory can sometimes fail to establish the trait that should be common for most managers. This theory can be best suited for organisations where there is enormous customer demand for their products/services, and therefore the need to control productivity within the workforce must be strictly looked at.
4. The action centred leadership theory focuses on the relations between managers and leaders and how they can control the three factors that control this model – team, task and individuals. The aim of this theory is too guarantee the success of leaders and managers to be able to achieve the organisation’s goal and objective, to build solid principles, improve the quality of the working environment and to develop teams and productivity. This model is best suitable to businesses where there is a sense of efficiency and support between groups, the results from this model will be that leaders will see all departmental teams develop and coordination between each level to further productivity.
Management theories:
1. Classical Management theory is based on the idea that employees only have physical and economic needs of an organisation. It has been noted that most organisations do not take into account what could be considered the social needs of the worker and ensuring the satisfaction of their job. Instead, they direct their notions on the emphasis on specialising in labour skills, seeing to centralising leadership, maximising organisationally profits and the making of decisions. This theory is mainly connected to organisation’s where their only emphasis is in regards to productivity and not the needs of the worker.
2. The behavioural theories of management are seen as the behavioural of leaders and how they approach a challenge if they choose not to use the situational approach. These types of managers are task-oriented and find themselves not being a relationship with mind, but this mindset can differ depending on the leader who management is working with. The behavioural theory of management can also be connected to human relations, as this addresses and focuses on the better understanding of human behaviour within the organisation. These theories can be seen as being better suited for organisation’s where management focuses on achieving the goals and objectives of the company by ensuring that they empower and motivate their employees.
3. The contingency theory of management looks at the leadership style which is applied to within the business; this theory is only applied when management look to increase the business productivity above all and meet the goals set by the organisation. The task of management when using this theory wants to improve the working environment of the organisation by developing a good relationship with the employee so that it motivates the employees towards accomplishing the goals of the organisation.
4. The chaos theory of management describes the chaos or interruption which arises from a change in the public demand or a slowdown in the economy. This model is connected to control when their employees are adequately skilled in handling when a critical situation arises.
5. The objectives of management states to improve the operation of the business by defining their goals, these objectives are approved upon by management and employees of the organisation. Start-up business finds that they use this model as management see that it’s ideal to include their employees in the decision process of the market.
6. The transactional theory of leadership is similarly known as managerial leadership; it sees to focus on the supervision, organisation and performance of the business. This model promotes management to use the reward and appraisal system for employees within their department. This theory is suitable for companies where the management team purposes to improve the efficiency of the organisation and to also develop a sense of right relations with their employees.
M2. Assess the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches to situations within the work environment.
All the theories mentioned above have their strengths and weaknesses these are explained below:
Situational Leadership Model
| Strengths: | Weaknesses: |
| •no one style of leadership provides the best possible selection of multiple leadership styles instead of developing the same processes. |
You have to be 100% sure of the quality of your product to give a money-back guarantee. This describes us perfectly. Make sure that this guarantee is totally transparent.
Read moreEach paper is composed from scratch, according to your instructions. It is then checked by our plagiarism-detection software. There is no gap where plagiarism could squeeze in.
Read moreThanks to our free revisions, there is no way for you to be unsatisfied. We will work on your paper until you are completely happy with the result.
Read moreYour email is safe, as we store it according to international data protection rules. Your bank details are secure, as we use only reliable payment systems.
Read moreBy sending us your money, you buy the service we provide. Check out our terms and conditions if you prefer business talks to be laid out in official language.
Read more