Biometric Authentication Systems
The biometric authentication systems are automatic approaches of recognising a specific person also verifying the individuality of a required person. These systems are created on a biological and their behavioural physical appearance, as such voice, face, iris and fingerprints. Identity authentication in the computer authentication systems have conventionally based on a device that has a single key, chip or magnetic card, also another popular authentication method is PIN and passwords. Items like cards or keys are often stolen or lost and password are frequently forgotten or are revealed to other people.
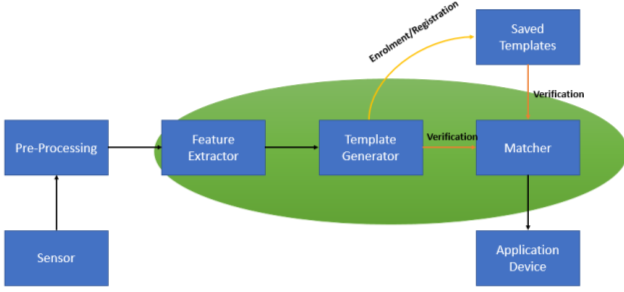
The biometric authentication system requires matching a registered biometric sample in line with the newly captured biometric scan e.g. an iris scan that was captured during registration.
During Registration/Enrolment a feature of the human attribute is captured and then it is processed by the computer. Once that has been completed then the computer will store the data for future comparison.
The biometric system recognition utilizes in Identifying/ID mode in which the biometric authentication system recognizes a certain person from the whole registered populace by looking through a database for a specific match solely created on the given authentication method.
A biometric system can also be utilized in Verification mode in which the system validates a person/s that is claiming the identity from the registered pattern. This method is also known as “One to one” matching. In all of the network access and computer access surroundings confirmation mode will be utilized. For example, a user input in an account, inputs a username, or inputs a card but rather than inputting a password or a PIN the user will only require a touch with a finger or just a scan of their iris at a camera is more than secure to grant access to the user.



Iris Recognition method utilizes the person iris in which the coloured part of the eye that surrounds the pupil, the patterns within the Iris are known to be unique. The patterns of the iris are retrieved by a video based captured image system. The scanning devices that are utilized within the authentication application for numerous years. As per the findings the iris authentications systems have heavily reduced in price and this drop is known to drop further. This type of technology will work best with both the identification and verification mode.
Face Recognition method is the authentication of a specific person which identified by their facial image, this can be done in more than one way; one method is done by taking an image of the person face within the perceptible field utilizing a camera or it can also be captured with the infrared patterns of facial heat emissions.
The Finger Geometry And Hand is utilized to accomplish a unique personal identification. The system can measure/capture also the physical features of the hands or the fingers. This type of identification or authentication is utilized because every person’s hand has a different shape also that the shape or profile of the hand never varies despite of the age. The manufacturers of the devices show that the cross over accuracy is about .1%. These types of figures are difficult to achieve in reality. The FRR of 10% and FAR 3% within the middle security threshold are more accurate and realistic.
Signature Verification/Dynamics is based on the subtleties of creating a signature. This type of technology utilizes the dynamic analysis of the signature in order identify or authenticate the specific person. This system will measure the pressure, speed and the angle utilized by the person when the signature is created.
DNA method is based on the analysis of a specific persons DNA. In order to person the DNA analysis the person will need to give some of their cells; e.g. hair strands or even samples of skin. The analysis of the DNA can take a longer time compared to the rest of the authentication methods. This is the main reason why the method is not used very often. Though this method would be a great means to provide authentication as every person has a unique DNA.
In authentication systems there are 2 sorts of errors:
|
Rates / Devices |
A |
B |
C |
|
FAR |
.1% |
.2% |
6% |
|
FRR |
30% |
8% |
40% |
*The tables displays the FAR and FRR rates for 3 devices which are set to the highest security level. (Figures are rounded)
|
Rates / Devices |
A |
B |
C |
|
FAR |
0% |
.001% |
1% |
|
FRR |
70% |
50% |
60% |
The errors that are indicated are quoted by the manufactures of the system and the ERR typically is <1%, which would show that the biometric system are truly accurate.
The biometric authentication system has number of advantages; Biometric systems only grant access to people as it cannot authenticate a computer system as they are based on public key or IP address. The characteristics of biometrics which used within authentication systems are unique for every person.
The disadvantage of the iris scanner is that it can become affected by the change in the outer lighting or anything that is obscuring the lenses, eyelashes or even if a reflection is made then it can fail the authentication process. The iris authentication can fail on a number variation as such the pupil deforms non-elastically which can affect the identification of the specific person. The iris authentication method is known to have more failure enrol rates as with some of the other photographic authentication systems. There are other authentication/identification infrastructure such as ID cards or national resident database then the civil right has shown that the iris identification technology may help the government to track specific individuals and beyond.
The biometric authentication system that utilize behavioural (signature or voice, etc..) and physiological traits (iris, face etc..) are known to become quite popular and used in number of applications to increase the strength of the security systems. Old systems are not able to distinguish between an intruder whom is fraudulently accessing a system or an authorised person that is actually trying to access their personal information. Biometric authentication systems are much more convenient to utilize due them not needing password to enter which eliminates the factor of forgetting passwords another point is that you can use a single biometric authentication to secure various accounts. There are eight types of attack in the biometric authentication systems in which they are divided into two different categories: Indirect attacks and Direct attacks.
Direct attack is referred to that attack that does not require any knowledge about the specific systems operations such as the matching algorithm utilized and the vector format feature. This involves type 1 attack which known as the “sensor attack”.
The type one attach is the sensor module which is very vulnerable to the attack which is commonly known as the “Attack the sensor”. In this attack a duplicated biometric trait is used such as an artificial facial image and finger which is then presented to the sensor by the imposter to bypass the system recognition. The hacker or in this case an imposter can also damage the recognition physically and take over the system with false access requests.
The direct attack is not like the indirect attacks. These attacks are where the information about the internal workings of the biometric authentication systems is required to process an attack successfully. This attack requires the remaining seven points which can then be attack by the so-called imposter.
Type 2 attach is when a sensor receives new biometric data which is then sent to the new data extractor module to pre-process through the communication channel. This channel can be located in the middle of the sensor and the feature extractor modules. This then stopped to steal the biometric data and stored onto another server. Once this been done then the diametric data can be replayed to bypass the sensor.
The module of the feature extractor can be exposed to the type 3 attack which can be known as “Attack on the features ex module”. In this attack the imposter pressurizes the extractor module to make the feature values which are chosen by the imposter.
The type 4 attack has similarities to the type 2 attack, but the only difference is that the imposter can take over the communication channel in the middle of the extractor and matcher module to steal the features of the values of the authentic user.
The matcher module is exposed/weak to the “attack on the matcher module”. It is attacked to create the highest matching scores which are selected by the imposter to bypass the system.
This attack takes place when the intruder weakens the security of the database by importing new templates. It is not easy to instruct the attack system database because some templates are secured by a digital mechanism like watermarks or steganography.
This attack can only be possible when the template is transmitting from the communications channels through matcher module and system database. This happens when the imposter tampers or modifies the contents of the template transmitted. The imposter then takes over the channel to replace, steal or even alter the template.
In this attack the imposter can overrule the declared results and the imposter can tamper with the match scores that are sent through the cannel. Then the match scores change the original decision to accept or reject the module matcher.
The accurateness of the biometric authentication systems is not flawless, then there are other established biometric authentication systems that are available. The appropriate application and design of the systems can for sure surge the entire security of the specific system is being implemented. Fingerprint scanners can be more effective to grant access/entry to a specific person where their other security measures taken such are work of place with well monitored area to avoid anyone from getting access to it and avoid identity crises. The iris scanner is the most effective because it cannot be hacked or replaced nor copied as every pupil of every person is unique and cannot be duplicated. I would recommend any medium size business to use the iris scanner to maximise their security.
You have to be 100% sure of the quality of your product to give a money-back guarantee. This describes us perfectly. Make sure that this guarantee is totally transparent.
Read moreEach paper is composed from scratch, according to your instructions. It is then checked by our plagiarism-detection software. There is no gap where plagiarism could squeeze in.
Read moreThanks to our free revisions, there is no way for you to be unsatisfied. We will work on your paper until you are completely happy with the result.
Read moreYour email is safe, as we store it according to international data protection rules. Your bank details are secure, as we use only reliable payment systems.
Read moreBy sending us your money, you buy the service we provide. Check out our terms and conditions if you prefer business talks to be laid out in official language.
Read more