Abstract
With the exponential growth in usage of smart phones and smart devices and the search engine technologies, Augmented Reality is claimed to be the most disruptive technologies of this decade. Industries and people have adopted AR to enhance user’s perception and help them feel, see and feel the real world in a new and enriched way. AR will benefit the users in the field of healthcare, marketing, education, travel and manufacturing industry. In this case study we will analyze some recent applications of AR, how AR is disrupting the market, limitations of AR and what are the future opportunities for AR.
1. Introduction
What if we had technology to perceive completely computational elements and objects within our real-world experience, entire creatures and structures even that help us in our daily activities, while interacting almost unconsciously through mere gestures and speech? With such technology, mechanics could see instructions what to do next when repairing an unknown piece of equipment, surgeons could see ultrasound scans of organs while performing surgery on them, fire fighters could see building layouts to avoid otherwise invisible hazards, soldiers could see positions of enemy snipers spotted by unmanned reconnaissance aircraft, and we could read reviews for each restaurant in the street we’re walking in, or battle 10-foot tall aliens on the way to work.
Augmented Reality is a technology whose applications have been realized quite recently. AR has been recognized by Gartner as one of ten emerging technologies for 2019, and with today’s smart phones and AR browsers we are starting to embrace this very new and exciting kind of human-computer interaction. AR is becoming so popular because of its amazing ability to portray real-world situations on a user’s device and simulating real-world situations. This allows the user to experience the thrill that would have been possible only by physically reaching there.
1.1 Definition
“Augmented reality (AR) is the technology to create a next generation, reality-based interface” [78] and in fact already exists, moving from laboratories around the world into various industries and consumer markets”.(Van Krevelen & Poelman, 2010, p. 1) AR supplements the real world with virtual (computer-generated) objects that appear to coexist in the same space as the real world. AR was conceived in elementary form in the early 1970s and was recognized by MIT as one of the emerging technologies of 2007. Today, with the advent use of smart phones and the AR browsers people have started to embrace AR- the new and exciting type of computer-human interaction.
1.2 History
“On the reality-virtuality continuum by Milgram and Kishino [108] (Figure 1), AR is one part of the general area of mixed reality. Both virtual environments (or virtual reality) and augmented virtuality, in which real objects are added to virtual ones, replace the surrounding environment by a virtual one.” (Van Krevelen & Poelman, 2010, p. 1)
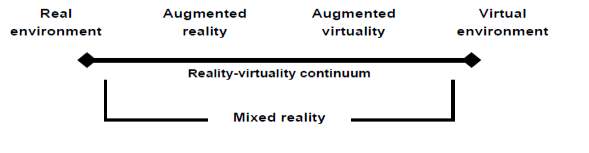
Figure 1. Reality- virtuality continuum (Van Krevelen & Poelman, 2010)
An AR system combines the real and virtual objects in a real environment, then aligns real and virtual objects with each other, and runs interactively in real time, in three dimensions. These three aspects of the definition of AR reflect the fact that AR is not restricted to any display technologies like the head-mounted display (HMD). AR can be applied well to all three senses- touch, smell and hear and thus, is not limited to visual senses. Mediated or diminished reality- removing the real-world objects and overlaying with virtual objects, is also considered AR.
2. Analysis
2.1 Characteristics
Augmented Reality is a variation of Virtual Reality, wherein a user is completely immersed in an artificial and synthetic environment and cannot see the real-world around him. However, AR augments the real world by superimposing the digital or computer-generated information like audio, video, images, and touch or haptic sensations. Contrary to VR, AR allows the use to see and feel the real world around him. Thus, AR augments and supplements the reality rather than replacing it with a virtual environment.
Three basic and fundamental characteristics of AR are-
“Augmented Reality, much like other graphical interfaces, gives us the ability to bring usable information into the visual spectrum in real time wherever we are.” (Augmented Reality: An Emerging Technologies Guide to AR).
2.2 Augmented Reality- Components
There are several components that are necessary to make the AR process a real-life experience. The core components for any fixed or mobile environment are basically divided into – hardware components and software components. Hardware components comprise of a computer- PC or a mobile device, a camera, a display screen, a complete network infrastructure, tracking and sensing systems like GPS or accelerometer and a marker. Markers are the physical objects or the places where the virtual and real world are amalgamated. The software component consists of a program or an app that runs locally on the PC or mobile device, a content server and internet connectivity.
2.3 Augmented Reality- Platforms
Gene Becker of Lightning Laboratories defines Augmented Reality as an emerging technology, a field of research, a high potential commercial industry and a new medium for creative and innovative expression. Thus, today AR is a well-known and sought-after technology and is basically sub-divided into four platforms based on the usage-
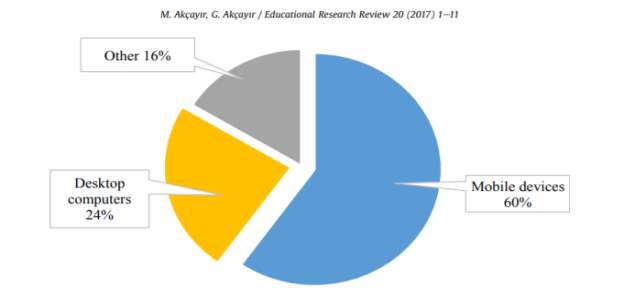
Figure 2. Distribution of AR Technologies used (Akçayır & Akçayır, 2017)
3. Augmented Reality Applications
Augmented Reality industry is expected to grow into a $90 Billion industry by 2020. Now a days, companies are using AR to engage their target customers. Every industry is experimenting around AR and is trying to build applications to provide interactive experiences to their customers. AR is used in Travel and hospitality industry, beauty and fashion industry, healthcare, education, marketing, journalism, travel, real estate, automotive and retail industry. Below are the five major industries that are currently using AR and have great potential to become more matured and successful with the use of AR.
AR is used in the healthcare industry to improve the patient diagnosis and treatment effectiveness. AR helps the healthcare organizations to make their processes and procedures more efficient and precise. For example, app like AccuVein is a hand-held scanner that works on AR, is used to project image over skin of the veins, valves and bifurcations underneath the skin to find a vein for the injection. Thus, saving time for the doctors and nurses and discomfort for the patient.
Many researchers and healthcare organizations have adopted AR to help the doctors to perform the surgeries more efficiently. Moreover, AR is useful in physical therapies, rehabilitation and for helping the stroke patients to perform better and monitor the patients’ progress at the same time. Patient’s 3D datasets is collected in real time, using noninvasive sensors like MRIs, CT Scans and ultrasound imaging. The data sets collected is then rendered and combined in real time with a view of the real patient. This provides the doctor with an ‘X-Ray’ vision inside a patient’s body. In this way doctors can perform a surgery with minimal incision and thus reduce the trauma of large incisions.
AR might also be helpful for general medical visualization tasks in the surgical room. Using AR surgeons can detect some features with the naked eye that they cannot see in MRI or CT scans, and vice versa. AR is also useful for training purposes where virtual instructions can remind and help a novice surgeon with the required steps for a particular surgery, without the need to consult a manual at the time of surgery. For example, Viipar, an AR app through which an experienced surgeon, in a different location can demonstrate to the person using Google Glass how to complete a surgery via the augmented hands that are projected onto the patient.
AR technology has already proved its value in the healthcare industry and will surely bring much better and bigger innovations in the coming years. As the healthcare costs continue to grow, AR will play an important role to help prevent and control diseases and cure millions of people more efficiently. The future of AR is bright in the healthcare sector, with the revenue opportunity estimate of $1.2 Billion in 2020 and then increase to around $5.1 Billion in 2025.
Marketing is a strong arena for augmented reality and the industry is exploiting AR to boost their sales with attractive product catalogs and interactive apps. Marketing industry is focusing on increasing their sales and expand their customer database with augmented reality. With the use of AR, the companies can focus on providing a real-world experience to their customers, wherein the customers can feel and try the product they wish to buy. Through AR marketing the companies can create powerful emotional connections with the customers- the prime marketing strategy.
AR helps in capturing the customers preferences and selections and customize a product as per the customer needs. With AR, sharing the product catalogue is much easier and better than before and the customers can also access the latest up to date information about the products, trends, promotions or deals. For example, AMC theaters leverage the augmented reality technology for marketing the movies. People can use their smartphones to point at the posters, either in magazines or theatre lobby and it would immediately show all the information about the movie- release date, trailer and movie cast.
IKEA, the world’s largest furniture retailer, also recognized the value of AR Marketing and launched an app- Ikea Place. The app was built using Apple’s ARKit technology and helps the customers preview how the furniture look on their smartphones, before buying it. The app- ‘Ikea Place- Try before you buy’ is true to scale and provides an interactive experience to the customers. It is a magical experience where customers can see and feel as if the objects or furniture are real and walk around them.
The Dulux Visualizer app helps the customers to try out a shade of paint for their room instantly, before buying the paint. Customers can use their smartphones to explore different colors and shades with just a tap of the screen.
Figure 3. Dulux Visualizer App (“The Dulux Visualizer App,” 2017)
Augmented Reality is giving a new dimension to learning and education- from being a conventional industry to a more advanced and state-of-the-art industry. Education industry uses AR to overlay engaging 3D models on the texts and pictures to make the learning more immersive and interactive. Lab safety information is displayed through AR so that the students can us the equipment safely. AR can also help the hearing-impaired children to understand and learn how to write a word or a phrase, by providing video overlays for words. Professors and teachers can provide real-time instructions to the students for their assignments using the AR video overlay technology.
Today more than 80% of the young people own smartphones. Thus, the potential of combining the Augmented Reality and the smartphones is huge. AR can help the students with extra digital information about any subject and make them understand the concepts better. For Example, AR classrooms, where AR is used to provide a short bio of a person, some fun facts, historical data or visual 3D models to help students understand a subject or concept better.
QuiverVision, a New Zealand based company, originally called coIAR has received overwhelming feedback and awards at world conferences for the use of AR for educational purposes. It is a 3D augmented reality coloring app that produces educational content that supports learning in fun and stimulating ways. The app combines physical coloring with state-of-the-art AR technology to provide the students and interactive learning experience, where every coloring page can be brought to life.
Today, Google Translate (iOS/ Android) is extensively used for studying the foreign languages without a dictionary or bulky websites. By using the ‘AR mode’ of Google Translate, students can instantly search the unknown words. It also helps the students and tourists to navigate through the cities abroad. Museums have also started using the AR, wherein the students or people can use the AR headsets and learn about the history of the sculptures and monuments.
Regardless of the rise of AR technology in other industries, use of AR in education industry is still new and uncertain. Though the possibilities are great, still the teachers need to grab student’s attention to motivate them to use the new AR tools and apps. Moreover, it is an expensive technology and thus, not accessible to all the students. At times AR apps consume more time and the technical problems may distract a student’s attention.
Travel and hospitality industry have leveraged AR to build apps that helps the people explore any place more easily. Tourists are unlikely to know much about the place they are visiting, and many a times miss the local events or the best local food restaurants. This lack of knowledge and information is a missed opportunity for both the traveler and the local businesses.
AR helps solve above problem in various ways. For example, a tourist can use an AR app by placing the camera viewfinder over a New York street to find out the information about the restaurants, shops and nearby events. With a more matured and sophisticated AR app people could even buy tickets to a concert or make restaurant reservations.
Google’s augmented reality app- Worldlens lets the users aim their smartphones at the street signs and then automatically translate them, for their better understanding and thus help the international travelers. UK’s Gatwick airport passenger app won the Mobile Innovation of the year award in 2018, for its creative and innovative use of AR technology. The app helps the passengers navigate through the airport with the help of more than 2000 beacons throughout the airport’s terminals. The app helps the passengers use the AR maps from their mobile phone to navigate in the right direction.

Figure 4. Gatwick Airport Passenger App (“Gatwick’s Augmented Reality Passenger App Wins Awards,” n.d.)
Manufacturing industries are already progressing towards the age of ‘Industry 4.0- smart factories’ with the use of IoT, Cloud Computing, Smart devices, 3D Printing and Augmented Reality. Augmented Reality is already a great hit in the manufacturing industry and in future is going to assist the production lines. AR, together with VR is growing from a $5B industry in 2016 to $29.5B industry in 2019. There are three main applications of AR in the manufacturing industry:
In 2016, DAQRI launched a smart helmet for the heavy industry. The helmet is operated by an Intel processor and has 3 different cameras- high-resolution, low-resolution and infrared. The helmet provides the user with the 4D work instructions, thermal vision and remote support. It is a single device with endless usefulness.
AR is also used for quality control by diagnosing each stage of the manufacturing process. For Example, Porsche upgraded its factories in Leipzig and Zuffenhausen and named it “Porsche Production 4.0” (Editor, 2017). The quality center uses AR to discover immediately, even minor deviations from the standards and thus making it possible to see monitor quality control throughout the complete production cycle.
Manufacturing Industry is leveraging Augmented Reality in almost all of its processes and techniques. The workers can use AR to overlay text, stats and information relevant to them. For example, pointing the AR enabled gadget (mobile phone, tablet) at a furnace or a machine the workers can gain information about the current furnace temperature, and warning the worker to be cautious if it is hot and unsafe to touch. In future, AR will provide the workers will everything that’s happening around them- from their personal safety to the quality control process. Below are some ways in which AR will influence the manufacturing industry and thus disrupt the complete manufacturing industry:
For example, DHL, the popular shipping and freight service is testing a new mobile AR system. “DHL Supply Chain is expanding vision picking pilots with Google and Vuzix smart glasses, and Ubimax software over the next six months across different industries” (“DHL | Press Release | English,” n.d.)
AR devices are now used by the maintenance crew to view which equipment needs servicing and has any potential issues. Maintenance of any equipment is all about speed and accuracy. The AR system relays information about the operation time, thresholds and potential points of failure. This would provide quicker response and recovery times, faster repairs and thus, overall better operations. For example, Mitsubishi Electric created a new 3D-model AR based maintenance support system, for inspection. The model enables a technician wearing the smart glasses to confirm the sequence of the inspection on an AR display device and then enter the results by voice commands.
AR can be used in designing of cars, planes and other heavy machines that have a difficult construction process. AR can eliminate some of the tedium of the traditional design process by augmenting and enhancing the design process and, at the same time, also streamlining the communication and collaboration between different parties involved. AR models help to estimate the functionality of the design and to optimize is before the actual manufacturing.
Below are the key benefits of using AR, over the traditional product design and development:
Use of AR in the manufacturing industry is extensive as it helps in increase in production, reduce the final costs of production and prevent errors. AR not only improves the quality of a product but also improves the complete manufacturing process, employee skills and maintenance. AR tools can be used for the complete product life-cycle. The technology is cost effective, scalable and worth the investment in any kind of production unit.
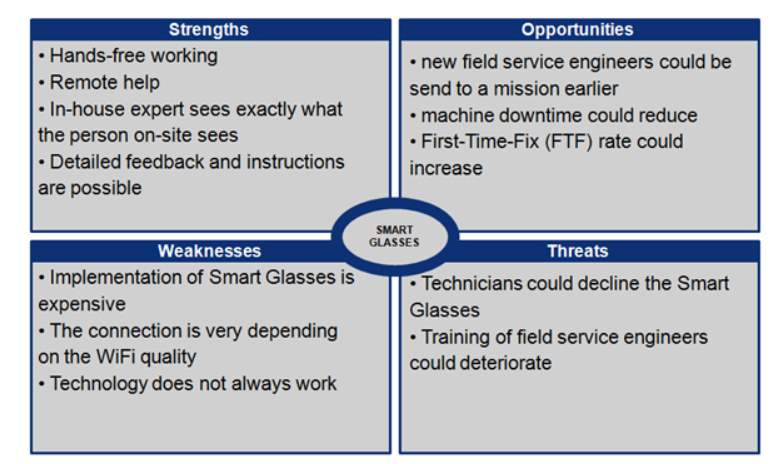
Figure 5. SWOT Analysis for use of AR in Manufacturing
The above cases are just few examples of the true potential of AR in the manufacturing industry. It will take some time to move from the current scenario to a more matured and state of the art AR system for the manufacturing industry and moreover cyber-security will play a vital role in future, since almost all the devices will be connected.
5. Limitations
Augmented Reality undoubtedly is an emerging and fascinating technology that attracts the industries and customers towards its various applications. AR has come a long way from its roots in VR and many a times when people considered VR and AR as synonyms. Along this incremental development path AR overcome many challenges, as the technology is dependent on the smart devices and digital network. The future of AR is still bright, and the technology has great potential for growth. However, AR still faces some challenges and limitations that need to be addressed.
The first and the most important challenge is privacy. Some image recognition software, coupled with AR in future, will allow the users to point their phone at people and instantly see all information bout them from their Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter or other social media platforms. This could be seen a threat to a person’s personal information and privacy.
AR also faces challenges to render the digital data into meaningful graphics and then scaling it to fit to the size of the AR display screen. In case of the mobile phones, AR must work with the limited processing power and little storage. Moreover, many times AR cannot provide accurate tracking and orientation. The AR gadgets and devices used currently are bulky and not user-friendly. It is tough to setup, learn and use the AR systems and, many a times, the user is not free to move in the natural environment.
6. Conclusion
With so many advantages oin various industries and positive predictions of the market growth, undoubtedly, AR is a powerful technology that will give the early adopters an unprecedented advantage.
References
Akçayır, M., & Akçayır, G. (2017). Advantages and challenges associated with augmented reality for education: A systematic review of the literature. Educational Research Review, 20, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2016.11.002
DHL | Press Release | English. (n.d.). Retrieved December 19, 2018, from http://www.dhl.com/en/press/releases/releases_2016/all/logistics/dhl_rolls_out_global_augmented_reality_program.html
Editor, K. M. P. (2017, November 8). Porsche Adopts AR For Quality Assurance In Factory of the Future. Retrieved December 19, 2018, from http://metrology.news/porsche-adopts-augmented-reality-for-quality-assurance-in-factory-of-the-future
Figure 4. Percentage distribution for AR challenges in underground… (n.d.). Retrieved December 19, 2018, from https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Percentage-distribution-for-AR-challenges-in-underground-construction_fig3_326330440
Gatwick’s Augmented Reality Passenger App Wins Awards. (n.d.). Retrieved December 19, 2018, from https://www.vrfocus.com/2018/05/gatwick-airportsaugmented-reality-passenger-app-wins-awards/
Goguely, T. (n.d.). AR for Manufacturing | Atheer Augmented Reality. Retrieved December 19, 2018, from https://www.atheerair.com/ar-manufacturing/
The Dulux Visualizer App. (2017, September 19). Retrieved December 19, 2018, from https://www.dulux.co.uk/en/articles/dulux-visualizer-app
Van Krevelen, R., & Poelman, R. (2010). A Survey of Augmented Reality Technologies, Applications and Limitations. International Journal of Virtual Reality (ISSN 1081-1451), 9, 1.
You have to be 100% sure of the quality of your product to give a money-back guarantee. This describes us perfectly. Make sure that this guarantee is totally transparent.
Read moreEach paper is composed from scratch, according to your instructions. It is then checked by our plagiarism-detection software. There is no gap where plagiarism could squeeze in.
Read moreThanks to our free revisions, there is no way for you to be unsatisfied. We will work on your paper until you are completely happy with the result.
Read moreYour email is safe, as we store it according to international data protection rules. Your bank details are secure, as we use only reliable payment systems.
Read moreBy sending us your money, you buy the service we provide. Check out our terms and conditions if you prefer business talks to be laid out in official language.
Read more